Tagged: “Dr. Richard Fitzgibbons”
Shedding Light on “The Dark Side of Forgiveness”
On December 16 this year, I had an interview with Justin Ballis, writer for the London-based magazine, What the Doctors Don’t Tell You, that aims to provide evidence-based holistic solutions to illness. Mr. Ballis was one of the most informed interviewers on the topic of forgiveness whom I have ever encountered. The interview covered an impressively wide range of topics on forgiveness, one of which centered on criticisms leveled against the practice of forgiving those who hurt us. In his researching the skeptical views, Mr. Ballis came across a journal article on “the dark side of forgiveness” by Dr. James K. McNulty:
McNulty, J.K. (2011). The dark side of forgiveness: The tendency to forgive predicts continued psychological and physical aggression in marriage. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 37, 770-783.
This discussion with Mr. Ballis got me thinking: If well-informed journalists are aware of Dr. McNulty’s article, then it is important to have a thoroughgoing critique of that work, which is flawed in many ways. So, with this in mind, here is an excerpt (chapter 14) from my book with Dr. Richard Fitzgibbons, Forgiveness Therapy (American Psychological Association, 2015), in which we examine the science behind this work:
McNulty (2011) claimed to have found scientific support for the view that forgiving within marriage perpetuates injustice. Seventy-two first-married couples took part in a survey in which they responded to hypothetical situations regarding forgiveness. For example, one of the partners asks the other to mail a very important package which the other partner then forgets to do. On a 1-to-7 scale, the respondent reports the degree of forgiveness that he or she would offer to the forgetful spouse. We have four criticisms of the study’s conclusions: a) The questionnaire was very short (five items); b) the questions were all hypothetical and not actual situations in the marriage; c) only one of the hypothetical scenarios is actually serious (an alleged affair), and d) the questionnaire simply asks the participant if he/she would forgive without ever defining the term. The forgetful spouse who failed to mail the package did not act with intent to harm. The one choosing to have an affair did. In other words, some respondents may be confusing genuine forgiveness with excusing or “letting go.” This is a serious flaw to the work (failing to distinguish related but quite different terms) that could have been overcome by asking people what they mean when they use the word forgiveness. The findings could reflect this: Those who score high on this scale are doing the most excusing or condoning, which could make them vulnerable to further abuse. In other words, those who excuse may not seek a proper justice solution upon “forgiving.”
So, there is our critique. My conclusion? It is this: If there is a “dark side” to forgiveness, the above study is not the one to show it.
Robert
Forgiveness: “Groundbreaking Scientific Discovery”
A cutting-edge organization in California that sponsors groundbreaking scientific discoveries has launched a new service called Greater Good in Action and added forgiveness to its list of practices that can help you improve your social or emotional well-being or the well-being of others including your children.
 The Greater Good Science Center (GGSC) at the University of California, Berkeley, not only studies the psychology, sociology, and neuroscience of well-being but also “teaches skills that foster a happier life and a more compassionate society–the science of a meaningful life.”
The Greater Good Science Center (GGSC) at the University of California, Berkeley, not only studies the psychology, sociology, and neuroscience of well-being but also “teaches skills that foster a happier life and a more compassionate society–the science of a meaningful life.”
The Greater Good in Action initiative adds forgiveness to its list of established practices that include compassion, generosity, gratitude, honesty and others. It is a new addition to a service the organization began in July of 2017, called Raising Caring, Courageous Kids that is designed to help parents raise kids of high character who treat others with compassion and respect.
In its inaugural forgiveness practice called Introducing Kids to Forgiveness, Greater Good in Action cites the pioneering forgiveness work of psychologist Robert Enright, Ph.D., and psychiatrist Richard Fitzgibbons, M.D. (co-authors of Forgiveness Therapy, a manual providing instructions for clinicians who want to incorporate forgiveness interventions into their therapy with clients.
Referencing Dr. Enright’s years of hands-on experience teaching children about forgiveness (he has developed 17 Forgiveness Curriculum Guides for kids in pre-school through 12th grade that are being used in more than 30 countries around the world), Greater Good in Action links readers to a separate dissertation on Dr. Enright’s insights into how to help children and adolescents learn and practice forgiveness.
That work concludes that “a wide range of studies have found that forgiveness programs can help kids of different ages feel better, strengthen their relationships, and improve their academic performance.”
Because conflict is inevitable, teaching children about forgiveness early on
may indeed be a path toward building communities
of people who prize and cultivate peace.
Maryam Abdullah, Ph.D., Parenting Program Director at Greater Good
and a developmental psychologist with expertise in parent-child relationships.
The practices provided by Greater Good in Action are for anyone who wants to improve his or her social and emotional well-being, or the well-being of others, but doesn’t necessarily have the time or money to invest in a formal program. Through its free online magazine Greater Good, the GGSC provides articles, videos, exercises, quizzes, podcasts, workshops and more for parents and families to help them foster positive attributes like forgiveness in themselves and their children.
How Forgiving Are You?
When someone does you wrong, are you more likely to turn the other cheek or slash their tires? Take the Greater Good Forgiveness Quiz to find out.
Have you or your colleagues worked on forgiveness with people who have significant mental health challenges, such as major depressive disorder or bi-polar disorder?
Yes, my colleague, the psychiatrist Dr. Richard Fitzgibbons, has case studies of this kind in our book, Forgiveness Therapy, 2015. Not all people who show major depression or bi-polar disorder are excessively angry with other people, but Dr. Fitzgibbons does screen for this. When people with significant mental health challenges show unhealthy anger caused by unjust treatment from other people, then Forgiveness Therapy is warranted and shown to be effective in these case studies.
For additional information, see Forgiveness Research.
The History of Forgiveness Therapy
The prominence of forgiveness and forgiveness therapy in the field of psychology over the past few decades has been well-documented in the scientific literature. Also well documented has been the pioneering and groundbreaking forgiveness work of Dr. Robert Enright within that movement. Here are pertinent milestones: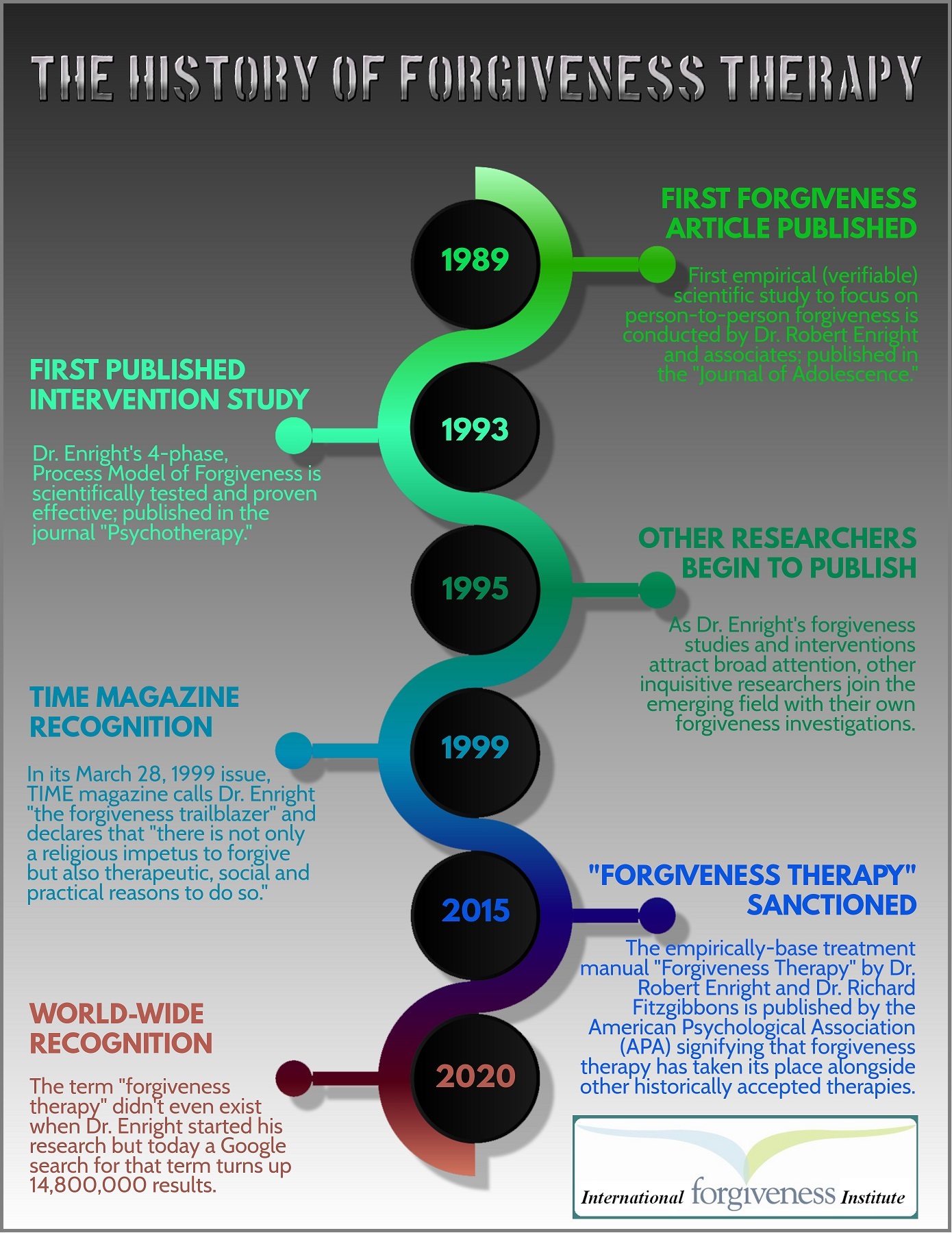
Rage Reduction Through Forgiveness Education
By Dr. Robert Enright and Dr. Richard Fitzgibbons
After massacres in El Paso, TX, and Dayton, OH, in which 29 people died, President Donald Trump made a number of sensible recommendations to address violence and mass murders in the United States. He has been criticized for not calling for stricter gun controls but his words went to the heart of this crisis of hatred and violence:
“We must recognize that the Internet has provided a dangerous avenue to radicalize disturbed minds and perform demented acts. We must shine light on the dark recesses of the Internet, and stop mass murders before they start. . . We cannot allow ourselves to feel powerless. We can and will stop this evil contagion. In that task, we must honor the sacred memory of those we have lost by acting as one people.” (Read the Full Text Here.)
Below are our proposals for aspects of a comprehensive federal plan consistent with the President’s ideas. They are based on our combined 70 years of experience in research, education, and clinical work in uncovering and initiating treatment protocols in schools and in mental health treatment for excessive anger (or what psychiatrists call “irritability”).
Anger-reduction programs. The mental health field needs to develop protocols to identify individuals at risk for severe irritability and violent impulses. Next, empirically-verified treatment plans should be initiated for reducing intense anger and rage. Programs like this are rare in the mental health field.
A Secret Service report published last month, “Mass Attacks in Public Spaces,” found that 67 percent of the suspects displayed symptoms of mental illness or emotional disturbance. In 93 percent, the suspects had a history of threats or other troubling communications.
The mental health field needs to recognize that the training and ongoing education of health professionals has not been strong regarding the identification and treatment of irritability and violent impulses. So it is no surprise that the mass murderers of Sandy Hook, Virginia Tech, Lakeland, and Columbine had not been treated for their anger. We need training programs. They could be part of required Continuing Education credits for state licensure for psychiatrists, psychologists, and the other physicians who prescribe roughly 80 percent of psychiatric medications.
Our book, Forgiveness Therapy: An Empirical Guide for Resolving Anger and Restoring Hope, published by the American Psychological Association, can be one such training tool for mental health professionals. Forgiveness has been empirically verified to reduce unhealthy anger.
Education in schools. Education programs in schools could uncover and teach youth how to resolve intense anger and desires for revenge that lead to a sense of pleasure in expressing violent acts against others. Dr. Enright has worked to establish scientifically-supported programs for reducing anger in youth through forgiveness education curricula (from pre-kindergarten through grade 12). These educational guides have been sought by educators in over 30 countries. Dr Enright’s books, Forgiveness Is a Choice, The Forgiving Life, and 8 Keys to Forgiveness, can be used as anger-reduction tools with older high school students, college students, and adults.
Teach respect for persons. A key development for forgiveness education is a new perspective on humanity: all have inherent worth, even those who act unfairly. In other words, these programs not only reduce anger, and thus eliminate a major motivation to hurt others, but also engender a sense of respect for persons.
This combination of reduced irritability and a new perception of the worth of all could go a long way in reducing rage and thus in reducing mass shootings.
Regulate violent video games. Violent video-gaming and media violence have played a role in the behavior of mass murders. A continual exposure to gaming that denigrates others in a virtual environment is a sure way of damaging respect for persons. Such “games” have courageously been identified by the President as factors in the epidemic of violence. Rather than teaching the importance of mastering anger without hurting others (character education), some games support the expression of rage and violence.
We need Federal laws. Youth are not allowed into movie theaters for X-rated fare. This should be the case with video games, which should be lawfully kept from youth when judged to have content that demonstrates and even encourages excessive anger. Parents should teach their children how to resolve their anger without harming others and should prohibit violent games in their homes. Violent games must have a warning that they could promote uncontrollable anger.
What about the guns? The President has identified essential issues that need to be addressed on the federal level to end the epidemic of massacres by individuals with severe, largely unrecognized and untreated, psychological problems.
While it is essential to try to keep guns out of the hands of those prone to act on their hatred, more important is the establishment of new anger control programs which will make for a safer America.♥
Robert Enright, Ph.D., is a Professor of Educational Psychology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and a Board Member of the International Forgiveness Institute, Inc.
Rick Fitzgibbons, MD, is a psychiatrist in Conshohocken, PA. They are joint recipients of the 2019 Expanded Reason Award, presented by the University Francisco de Vitoria (Madrid) in collaboration with the Vatican Foundation Joseph Ratzinger/Benedict XVI.
This blog originally appeared on the MercatorNet.com website on August 14, 2019.



