Forgiveness News
Could You Forgive the Drunk Driver Who Killed Your Daughter? This Mom Did Just That!
Meagan Napier and her best friend, Lisa Jo Dickson, were driving to Meagan’s home after an outing in Pensacola, FL on May 11, 2002. They never reached their destination.
Around 2:30 that morning (the day before Mother’s Day), a drunk driver hit the car Dickson was driving and rammed it into a tree. Both of the 20-year-old women were killed instantly. The 24-year-old drunk driver who caused the crash, Eric Smallridge, was eventually found guilty of DUI manslaughter (Driving Under the Influence of drugs or alcohol) and sentenced to 22 years in prison.
Unlike many too-often-repeated drunk driving crashes that result in deaths, the sentencing in this case was not the end of the story. In fact, it was just the beginning of an amazing story of commitment, forgiveness and lives saved. Please read on.
Shortly after Smallridge was sentenced, Meagan Napier’s heart-broken mother, Renee, made a commitment that something positive would result from the deaths of her daughter and her daughter’s friend Lisa.
So Renee began traveling to schools in her community to warn students about the dangers of drunk driving. As word of her compelling DUI presentations spread, she began receiving speaking requests from groups outside Pensacola and soon her part-time local commitment turned into a full-time nation-wide educational mission to prevent more unnecessary death’s like Meagan’s.
Still, as speaking engagements consumed more and more of her time, Renee felt there was something missing. She decided to visit the imprisoned man who was responsible for her daughter’s death. That initial meeting with Eric turned into a second meeting, and a third, and many more after that. What Renee discovered during those visits was that Eric was not the monster she had been imagining but was just like so many other hurt people who try to drown their anger and resentment in alcohol, in drugs, or whatever make-it-feel-good vice is available to them.
At the same time, Renee began learning about the healing power of forgiveness and eventually she forgave Eric–not because she felt sorry for him, but because she needed to release the pent-up anger and emotions in her own heart and mind that were taking their toll on her health and well-being.
“I could be angry, hateful and bitter,” Renee says. “But I didn’t want to live my life that way. There was no way I could move on and live a happy life without forgiving Eric.”
Renee said that prior to finding the courage to forgive Eric, she felt like she was the one in prison and that forgiveness “freed me from the darkest place I have ever been.”
Not only did Renee forgive Eric, she even approached the judge who had sentenced him to prison. Through a series of meetings and petitions (and with the strong support of the Dickson family), she somehow convinced the judge to cut Eric’s sentence in half–from 22-years to just 11 years–and to allow Eric to join her (bound by shackles and handcuffs) on many of her DUI presentations in order to also share his powerful testimony.
Even though Renee has forgiven him, Eric says he doesn’t know if he will ever be able to forgive himself. He says he is certain, however, that he will not drink alcohol ever again. Still on probation, Eric works at a Goodwill store and as a personal trainer. His mother serves as his unofficial chauffeur because his driver’s license, of course, was revoked.
“I was so selfish because I never considered what effect drinking and driving could have on someone other than me,” Eric tells audiences. “I made a bad decision, and now two young people are dead because of it.”
Though they admit that their relationship may confuse many, Renee and Eric agree that sharing their life-saving cause has helped them heal. They conclude each presentation with a compelling embrace.
Renee, who has become an award-winning speaker, is also the Founder and President of The Meagan Napier Foundation, a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization formed for two purposes: 1) to raise awareness of the dangers of driving under the influence of alcohol; and, 2) to promote forgiveness and healing. It operates under the banner of “Promoting Forgiveness • Mending Hearts • Saving Lives.”
“We live in a world with a lot of pain and heartache,” Renee says. “I want to promote love and forgiveness and help break that cycle of hatred.”
- Read more about Renee’s story.
- Read more about Eric’s story.
- Read more about Meagan’s story.
- Learn about the International Forgiveness Institute’s Safe Driving Campaign.
Forgiveness Therapy Proposed as Antidote for Traumatic Childhood Experiences
Forgiveness Therapy and forgiveness interventions developed by Dr. Robert Enright are being embraced in a just-released study as promising tools for effectively dealing with what the study calls a “major public health crisis.”
Researchers at the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (Tulsa, OK) have teamed up with those at Stanford University (Stanford, CA) to study the life-long adverse impacts of Early Life Adversity (ELA). The study is titled “Is There an Ace Up Our Sleeve? A Review of Interventions and Strategies for Addressing Behavioral and Neurobiological Effects of Adverse Childhood Experiences in Youth.” It was published just five days ago, March 13, 2020, in the empirical journal Adversity and Resilience Science.
ELA is the term for the negative experiences children may face or witness while growing up (sometimes also called Adverse Childhood Experiences—ACEs). These traumatic experiences include:
- emotional, physical, or sexual abuse;
- emotional or physical neglect;
- living in a household in which domestic violence occurs;
- growing up in household dealing with substance abuse or mental health problems;
- instability due to parental separation, divorce or incarceration;
- witnessing violence in the home; or,
- having a family member attempt suicide.
Any of those traumatic experiences can lead to what child development specialists call “toxic stress” if encountered by children without adequate adult support. Toxic stress can disrupt early brain development and compromise functioning of the nervous and immune systems. The more adverse experiences in childhood, the greater the likelihood of developmental delays and other problems that can cause life-long complications.
In fact, psychologists say, adults with more adverse experiences in early childhood are also more likely to have health problems including alcoholism, depression, heart disease, diabetes and other chronic diseases as well as impaired cognitive and social development. The report suggests that many adult diseases are, in fact, developmental disorders that begin early in life.
The new ELA publication describes and evaluates existing evidence-based interventions and their outcomes including Forgiveness Therapy. Three of Dr. Enright’s peer-reviewed empirical studies were examined and cited for achieving commendable outcomes compared to those of a control group:
- Female incest survivors (Freedman & Enright, 1996). Results: “significantly greater decrease in levels of depression and anxiety.”
- Women diagnosed with fibromyalgia who had experienced at least two ACEs in their childhood (Lee & Enright, 2014). Results: “increases in forgiveness toward their abuser, lower levels of state anger, and improvements in physical health related to their fibromyalgia symptoms.”
- Female Pakistani adolescents with histories of abuse (Rahman, Iftikhar, Kim & Enright, 2018). Results: Similar findings to the fibromyalgia study “suggesting that Forgiveness Therapy may uphold in a cross-cultural context.”
Those three intervention experiments by Dr. Enright and his research partners are the only Forgiveness Therapy examples cited in the 24-page ELA study that “have shown forgiveness therapy to be effective” in both physically and emotionally healthy ways. The ELA study also postulates that those interventions are effective because in Dr. Enright’s approach “the hypothesized mechanism behind forgiveness therapy involves cognitive restructuring of the abuser and events.”
Based on the evidence gather through this new ELA study, Forgiveness Therapy is one of the promising interventions for children who are experiencing toxic stress without appropriate support from parents or other concerned caregivers. That, they conclude, can help return a child’s stress response system back to normal while reducing negative mental and physical health outcomes later in life.
“Therefore, we conclude that they (Forgiveness Therapy interventions) are well-suited for and hold promise to exert immediate preventive and sustained changes in outcomes for maltreated youth.” – ELA study conclusion, March 13, 2020.
Why is this subject important? Why does it matter?
According to the World Health Organization, as many as 39% of children worldwide are estimated to experience one or more forms of early life adversity, placing a high economic burden on health-care systems—and society in general—through medical costs and lost productivity.
The mission of the Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR) is to “develop novel therapeutics, cures and preventions to improve the well-being of persons who suffer from or are at risk for neuropsychiatric illness.” Dr. Namik Kirlic, the LIBR Principal Investigator for the ELA study, is a clinical psychologist who has devoted his professional life to studying ELA interventions and how to optimize their positive outcomes. Other team members for the ELA study include Zsofia Cohen (Dr. Kirlic’s Research Assistant) and Dr. Manpreet Singh, a psychiatrist and medical doctor at Stanford Health Care.
MORE INFORMATION:
- Read the full, 24-page ELA study on Adverse Childhood Experiences.
- Learn more about Adverse Childhood Experiences on the Psychology Today website.
- Find out how toxic stress can have damaging effects on learning, behavior, and health across the lifespan at the Harvard University Center on the Developing Child.
- Read about Early Childhood Development on the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services Office of Early Childhood Development website.
Forgiveness: “Groundbreaking Scientific Discovery”
A cutting-edge organization in California that sponsors groundbreaking scientific discoveries has launched a new service called Greater Good in Action and added forgiveness to its list of practices that can help you improve your social or emotional well-being or the well-being of others including your children.
 The Greater Good Science Center (GGSC) at the University of California, Berkeley, not only studies the psychology, sociology, and neuroscience of well-being but also “teaches skills that foster a happier life and a more compassionate society–the science of a meaningful life.”
The Greater Good Science Center (GGSC) at the University of California, Berkeley, not only studies the psychology, sociology, and neuroscience of well-being but also “teaches skills that foster a happier life and a more compassionate society–the science of a meaningful life.”
The Greater Good in Action initiative adds forgiveness to its list of established practices that include compassion, generosity, gratitude, honesty and others. It is a new addition to a service the organization began in July of 2017, called Raising Caring, Courageous Kids that is designed to help parents raise kids of high character who treat others with compassion and respect.
In its inaugural forgiveness practice called Introducing Kids to Forgiveness, Greater Good in Action cites the pioneering forgiveness work of psychologist Robert Enright, Ph.D., and psychiatrist Richard Fitzgibbons, M.D. (co-authors of Forgiveness Therapy, a manual providing instructions for clinicians who want to incorporate forgiveness interventions into their therapy with clients.
Referencing Dr. Enright’s years of hands-on experience teaching children about forgiveness (he has developed 17 Forgiveness Curriculum Guides for kids in pre-school through 12th grade that are being used in more than 30 countries around the world), Greater Good in Action links readers to a separate dissertation on Dr. Enright’s insights into how to help children and adolescents learn and practice forgiveness.
That work concludes that “a wide range of studies have found that forgiveness programs can help kids of different ages feel better, strengthen their relationships, and improve their academic performance.”
Because conflict is inevitable, teaching children about forgiveness early on
may indeed be a path toward building communities
of people who prize and cultivate peace.
Maryam Abdullah, Ph.D., Parenting Program Director at Greater Good
and a developmental psychologist with expertise in parent-child relationships.
The practices provided by Greater Good in Action are for anyone who wants to improve his or her social and emotional well-being, or the well-being of others, but doesn’t necessarily have the time or money to invest in a formal program. Through its free online magazine Greater Good, the GGSC provides articles, videos, exercises, quizzes, podcasts, workshops and more for parents and families to help them foster positive attributes like forgiveness in themselves and their children.
How Forgiving Are You?
When someone does you wrong, are you more likely to turn the other cheek or slash their tires? Take the Greater Good Forgiveness Quiz to find out.
The History of Forgiveness Therapy
The prominence of forgiveness and forgiveness therapy in the field of psychology over the past few decades has been well-documented in the scientific literature. Also well documented has been the pioneering and groundbreaking forgiveness work of Dr. Robert Enright within that movement. Here are pertinent milestones: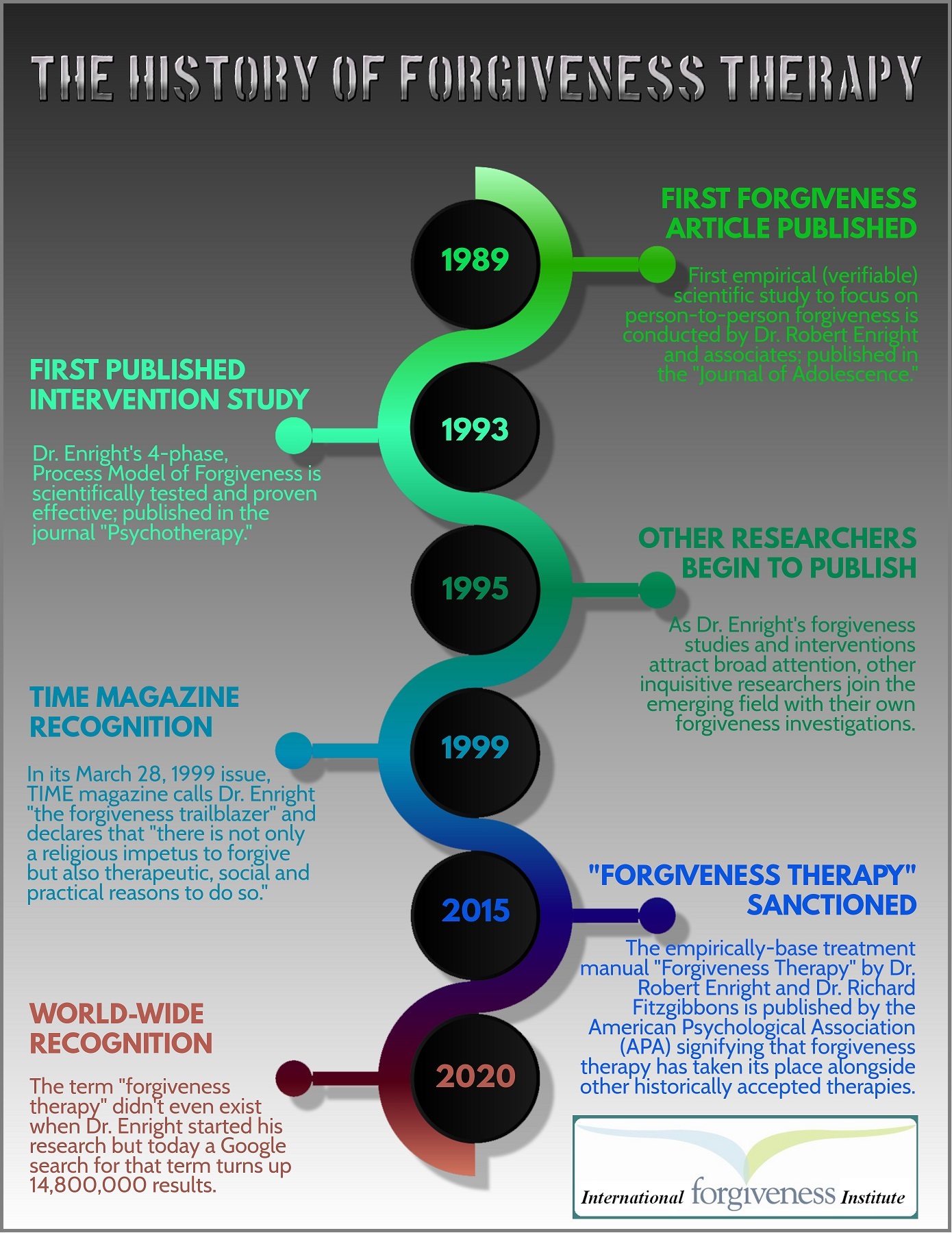
Forgiveness Spotlight: Dr. Jichan J. Kim
Editor's Note: This is the first in a series of articles that will focus on former students of Dr. Robert Enright who have continued their forgiveness research activities after graduation and who have made their own mark on the forgiveness movement.
Dr. Jichan J. Kim is a South Korean native who studied under Dr. Enright for four years at the University of Wisconsin-Madison where he earned both his Masters and Ph.D. degrees in Educational Psychology while at the same time pursuing research projects that led Dr. Enright to call him “one of the most prolific graduate assistants I’ve ever instructed.”

Dr. Jichan J. Kim
During those four years, the two researchers worked together to conduct numerous forgiveness-related research projects including a study that explored how graduate-level theology students in South Korea perceived the difference between divine forgiveness and human forgiveness. The results of that project were published just last month in the Journal of Spirituality in Mental Health.
After graduation, Dr. Kim left UW-Madison to become Assistant Professor of Psychology at Liberty University in Lynchburg, VA–a world-class Christian university founded by Dr. Jerry Falwell who gained international fame as an advisor to world leaders and who was named one of the 25 Most Influential People in America by U.S. News & World Report in 1983. Liberty University is one of the largest Christian universities in the world with more than 15,000 students attending classes on campus and more than 94,000 students taking courses through Liberty University Online.
At Liberty University, Dr. Kim teaches Introduction to Research, Directed Research, and Psychology and Christianity. In Spring 2020, he is teaching a
semester-long, special topics course in forgiveness,
for which he is very excited. He is also leading a Psychology Study Abroad Trip to South Korea in June 2020 where students will learn about: 1) the aspects of a collectivistic culture in contrast to an American individualistic culture; and, 2) how that culture views forgiveness and reconciliation.
The full course load complements Dr. Kim’s research activities. Since leaving UW-Madison three years ago, Dr. Kim has become even more intricately involved in forgiveness research and forgiveness education both in the US and in his home country of South Korea. His research and studies, for example, have:
- Examined the relationship between forgiveness and compassionate love;
- Explored the idea of the school as the Just and Merciful Community;
- Validated the Enright Self-Forgiveness Inventory;
- Examined subjective reasons why individuals forgive;
- Evaluated, together with his undergraduate research team at Liberty University, the effectiveness of a family-based forgiveness program with more than a dozen volunteer families; and,
- Explored the relationship between interpersonal, self-, and divine forgiveness.
“I give special thanks to Dr. Enright for introducing to me the beauty of forgiveness. I owe him a great deal and I will try my best to follow in his footsteps through a life dedicated to driving out hatred through forgiving love.”
Dr. Jichan J. Kim
 In addition to his UW-Madison degrees, Dr. Kim has received degrees from Harvard University (Cambridge, MA), Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary (South Hamilton, MA), and City College of New York. He also has extensive ministry experience in Madison, New York City, and Boston (serving various age groups in Korean immigrant congregations).
In addition to his UW-Madison degrees, Dr. Kim has received degrees from Harvard University (Cambridge, MA), Gordon-Conwell Theological Seminary (South Hamilton, MA), and City College of New York. He also has extensive ministry experience in Madison, New York City, and Boston (serving various age groups in Korean immigrant congregations).
Dr. Kim and his wife, Jieun, have three children–Yewon (Arianna), Juwon (Aiden), and Sungwon (Joseph). For the past several years, Dr. Kim has financially supported the International Forgiveness Institute with an automatic monthly donation through PayPal. He says he has two favorite quotes he tries to live by:
- Love never fails. (1 Corinthians 13:8)
- Forgiveness is offering love to a person in the face of injustice and at a time when that person is most unlovable. (Dr. Robert Enright)
Read more:
- Dr. Kim’s biography on the Liberty University website.
- Dr. Kim’s Ph.D. Dissertation on the effectiveness of anti-bullying programs.
- Abstracts of all Dr. Kim’s Forgiveness Research Studies.
- Inoculating Children Against Violence through Forgiveness Education – a Poster Presentation jointly developed by Dr. Kim and Dr. Enright.



