Tagged: “forgiveness therapy”
Does Forgiveness Work? Let’s Ask the Experts. . .
The benefits of forgiveness have been discussed and debated for centuries but scientific evidence that forgiveness actually “works” has been scant. All that has changed during the past few decades as legions of psychologists and clinicians have begun studying the ancient virtue from a stringently documented, peer-reviewed empirical perspective.
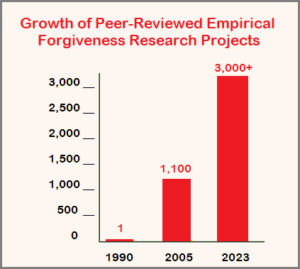 Dr. Robert Enright, an educational psychologist labeled the “forgiveness trailblazer” by Time magazine (and co-founder of the International Forgiveness Institute), published the first scientific study on person-to-person forgiveness in 1989. In the 15 years following the publication of that article in the Journal of Adolescence, the number of published forgiveness articles had jumped to more than 1,100. And today, researchers can pore through more than 3,000 published articles brandishing empirical evidence on the virtue of forgiveness.
Dr. Robert Enright, an educational psychologist labeled the “forgiveness trailblazer” by Time magazine (and co-founder of the International Forgiveness Institute), published the first scientific study on person-to-person forgiveness in 1989. In the 15 years following the publication of that article in the Journal of Adolescence, the number of published forgiveness articles had jumped to more than 1,100. And today, researchers can pore through more than 3,000 published articles brandishing empirical evidence on the virtue of forgiveness.
Here is a quick look at several recent research reports related to the benefits of forgiveness:
Forgiveness Reduces Suicidal Behavior
Suicide is the second leading cause of death for young adults and about 1,100 college students die by suicide each year (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). According to a study of 158 college students, all suffering from mild to severe depression, psychologists at East Tennessee State University found that:
“Students who are more capable of forgiving themselves and others after stressful life events or interpersonal problems have lower rates of suicidal behavior than their peers who are less able to forgive. This study points out that interventions that boost levels of forgiveness can increase self-esteem, hopefulness, positive emotions toward other people, and perceived self-control while reducing levels of depression, anxiety, and drug use.”
Source: Forgiveness, Depression, and Suicidal Behavior Among a Diverse Sample of College Students.
![]()
Forgiveness Education Program Reduces Depression, Anxiety, and Stress
After implementation of Dr. Enright’s Forgiveness Education curriculum for high school students in Turkey, study results demonstrated that:
“Forgiveness Education has led to significant decrease in symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. Conclusion: Forgiveness Education can be used effectively for adolescents in school settings.”
![]()
Even Brief Enright Forgiveness Education Programs Improve Health
Chinese college students demonstrated positive improvement in emotional health following brief (4 sessions compared to the normal 12 sessions) exposure to Enright Forgiveness Education curriculum classes. According to the study:
“The analysis of the pretest and post-test scores indicated that both the Enright Psycho-social Programme and the Chinese Value-oriented Programme had positive effects on improving participants’ general emotional forgiveness, decreasing their negative emotions toward the offender, and improving life satisfaction.”
![]()
Forgiveness Significantly Predicts Life Satisfaction
Researchers have begun to investigate the relationship between happiness and subjective factors like Forgiveness. A study with 380 students from different departments of Bursa Uludag University in Bursa, Turkey, found that:
“Happiness has been found to be negatively related to stress and positively related to positive emotions, satisfying relationships, self-esteem, forgiveness, self-compassion, and quality of friendships.Results in this study also indicate that forgiveness and life satisfaction are positively related and that forgiveness significantly predicts life satisfaction. For this reason, my results are important for psychological healthcare workers, who can include these variables into their supportive and preventive programs in order to assess important characteristics that contribute to good psychological health.”
Source: Predictive effects of subjective happiness, forgiveness, and rumination on life satisfaction.
![]()
In your research studies on forgiveness, what is the shortest intervention you have done that was successful in healing people from trauma? I am not talking about studies that others do with college students who are not traumatized in a psychiatric sense. Instead, I am talking about the kind of studies that have characterized your pattern of research as you work with traumatized samples.
The shortest amount of time needed for a successful forgiveness intervention with traumatized people is a study by Hansen and Enright (2009) in which our forgiveness process was implemented over a 4-week period, once a week for about an hour each time. This was done individually for each participant who was in hospice because of a diagnosis of terminal cancer. The participants, knowing they were dying, were very focused on the forgiveness intervention and their hope for the future increased as they forgave. I think the fact that they knew they were dying played a part in how quickly they forgave. In other words, 4-weeks for other traumatized populations probably would not be as effective because people need time to engage in the process of forgiveness.
This is the reference to that research in hospice:
Hansen, M.J., Enright. R.D., Baskin, T.W., & Klatt, J. (2009). A palliative care intervention in forgiveness therapy for elderly terminally-ill cancer patients. Journal of Palliative Care, 25, 51-60.
Here is a link to the research: Forgiveness Therapy as Palliative Care.
I recall that there was a quotation from Aaron Beck on the back cover of your first book for mental health professionals, Helping Clients Forgive. I no longer have that book cover. Would you please restate Dr. Beck’s quotation for me? It had to do with Forgiveness Therapy being stronger than Cognitive Behavioral Therapy when people are treated very unjustly by others.
Yes, I can provide that. Here is Dr. Aaron Beck’s quote on the back cover of the book, Helping Clients Forgive, by Enright and Fitzgibbons (2000): “Anger and the wish to punish a family member or friend for past grievances often remain resistant to the most useful cognitive-behavioral approaches. In this volume, Enright and Fitzgibbons show how forgiveness can help to finalize past resentment and allow people to lay their past grievances to rest. This is essential reading for anyone working with patients, as well as for those people who cannot relinquish past hurts.”
I am in graduate school studying to be a mental health professional. Held in high regard is the issue of insight. The point is to break down the psychological defenses so that the person now is aware of what is causing the anger or the anxiety or the discontent. How does forgiveness compare and contrast to the call for insight?
In our Process Model of Forgiveness, we have four phases. The first phase asks the client, when that client is ready, to see the amount of anger in the heart, caused by other people’s unfairness. There is more to this phase than just this, but my point is that we do make room, lots of room in fact, to explore the psychological defenses and to gradually see how current and persistent anger is connected to unfairness toward the client that might have occurred many years ago. Yet, awareness or what you are calling insight is only the beginning of Forgiveness Therapy. In other words, as a person now sees the depth of anger, what does the person now do to get rid of that anger? We find that insight is not enough. It is in deliberately reaching out to those who acted unfairly with the moral virtue of forgiveness, this has a way of softening the heart and thus reducing the anger to manageable levels. In other words, when deeply hurt by others, the inner trauma is not reduced to an important degree without forgiveness, which the client must freely choose for the self.
A Fireside Chat with Dr. Robert Enright
Dr. Robert Enright, the 2022 recipient of the prestigious American Psychological Foundation (APF) Gold Medal Award for Impact in Psychology, is featured in a just-released video presentation titled “APF at Home: A Fireside Chat with Dr. Robert Enright.”
The 1 hr. 25 min. fireside chat is part of a series developed by the APF that focuses on pioneering American psychologists “whose work has had a game-changing impact on the field of psychology.” Dr. Enright, founder of the International Forgiveness Institute (IFI), has been called “the forgiveness trailblazer” by Time magazine. His 37-years of forgiveness research has resulted in noteworthy innovations in forgiveness education and forgiveness therapy.
psychology.” Dr. Enright, founder of the International Forgiveness Institute (IFI), has been called “the forgiveness trailblazer” by Time magazine. His 37-years of forgiveness research has resulted in noteworthy innovations in forgiveness education and forgiveness therapy.
“Fireside Chats,” became a popular communications tool when President Franklin Roosevelt began a series of radio broadcasts that aired from 1933 through 1944. They were planned as conversations rather than stiff public speeches and were widely listened to because all the national radio networks carried them. In them, the President appeared to talk with his listeners rather than lecturing at them. And, yes, he actually sat next to the White House fireplace during the broadcasts.
 The fireside chats now being produced by the APF are intended to replicate that informal ambience. The latest interview, for example, features APF Trustee Dr. Katherine Nordal chatting with Dr. Enright. She asks him questions like how he selected forgiveness as the topic of his life’s work, how his Process Model of Forgiveness can be used in therapy interventions, and how forgiveness can become the crucial missing piece of the world’s peace puzzle. Dr. Enright answers questions submitted by viewers of the live presentation during the final 20 minutes of the session.
The fireside chats now being produced by the APF are intended to replicate that informal ambience. The latest interview, for example, features APF Trustee Dr. Katherine Nordal chatting with Dr. Enright. She asks him questions like how he selected forgiveness as the topic of his life’s work, how his Process Model of Forgiveness can be used in therapy interventions, and how forgiveness can become the crucial missing piece of the world’s peace puzzle. Dr. Enright answers questions submitted by viewers of the live presentation during the final 20 minutes of the session.
Dr. Nordal is well-equipped to conduct the APF fireside chat with Dr. Enright. She is a licensed psychologist whose distinguished career included owning and managing a full-time group private practice in Mississippi for 28 years. She spent another 10 years as Executive Director for Professional Practice for the American Psychological Association (APA) before retiring in 2018.
APF is the private grant-making arm of the APA and provides more than a million dollars annually in awards to fund research by psychologists and psychology students.
More Information:
A Fireside Chat with Dr. Robert Enright – Watch the entire presentation on YouTube.
APF at Home Fireside Chats – Watch all the videos in the series.



